Resources
SOLAR INVERTERS WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
“Solar inverters are the backbone of any solar power system, converting DC electricity into AC electricity that can be used by homes and businesses.”
Solar energy is a renewable and abundant energy source that has gained popularity in recent years. Solar energy is gaining popularity due to the decreasing cost of solar panels and the growing awareness of the environmental impact of traditional energy sources. However, solar panels only produce direct current (DC) electricity, which is not suitable for residential or commercial use. A solar inverter is required to convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into usable alternating current (AC) electricity.
What is a Solar Inverter?
A solar inverter is a device that converts the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity that can be used in homes and businesses. It is an essential component of any solar power system. The solar inverter takes the DC electricity generated by the solar panels and converts it into AC electricity that can be used by household appliances or fed into the electricity grid. Solar inverters come in different types, and the type of inverter used in a solar power system will depend on the application, size and complexity of the system.
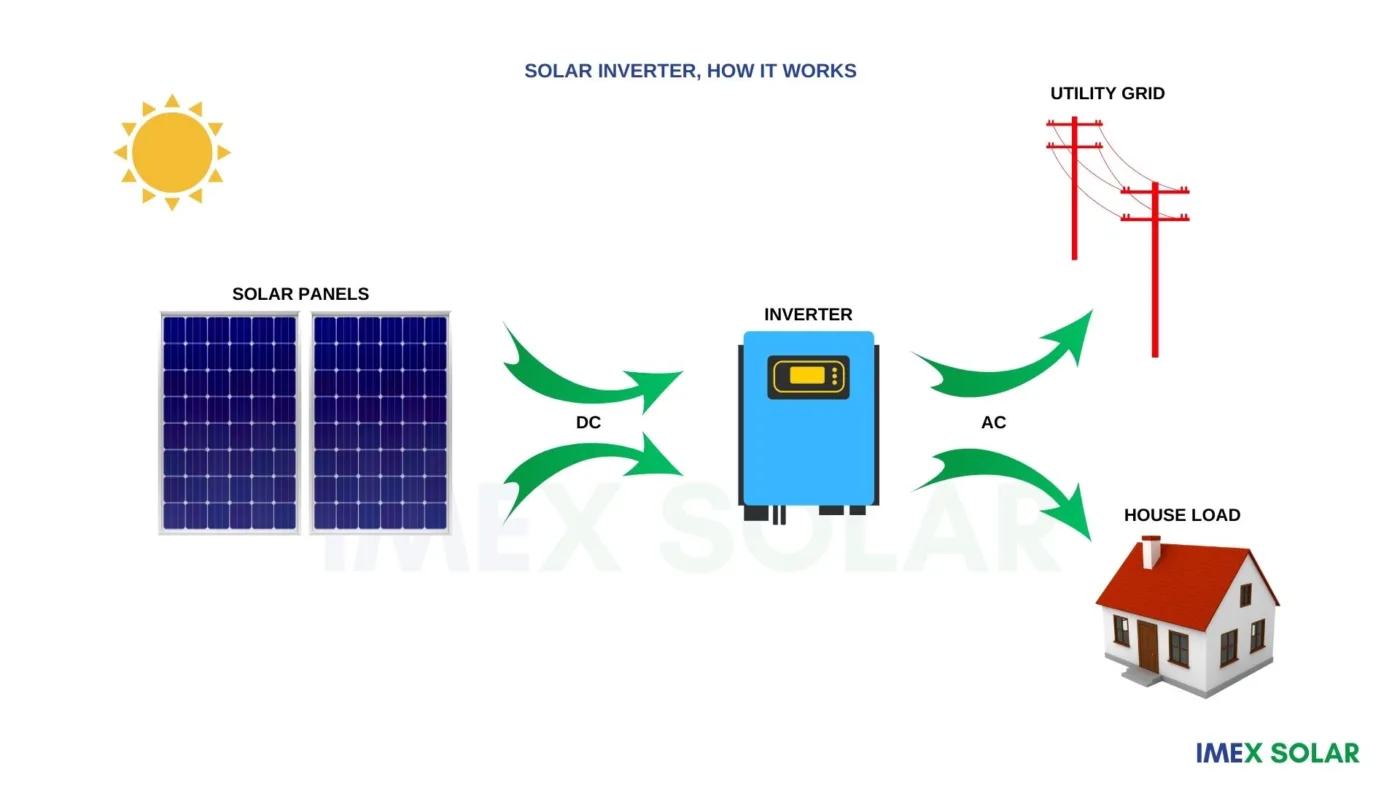
Types of Solar Inverters:
There are several types of solar inverters based on application and working principles.
In terms of application, there are three main types of solar inverters: on-grid, off-grid, and on-grid hybrid inverters.
On Grid Inverters:
On-grid inverters, also known as grid-tied inverters, are the most common type of solar inverter used in residential and commercial solar power systems. On-grid inverters are designed to work in conjunction with the electricity grid, allowing solar power systems to feed excess electricity back into the grid.
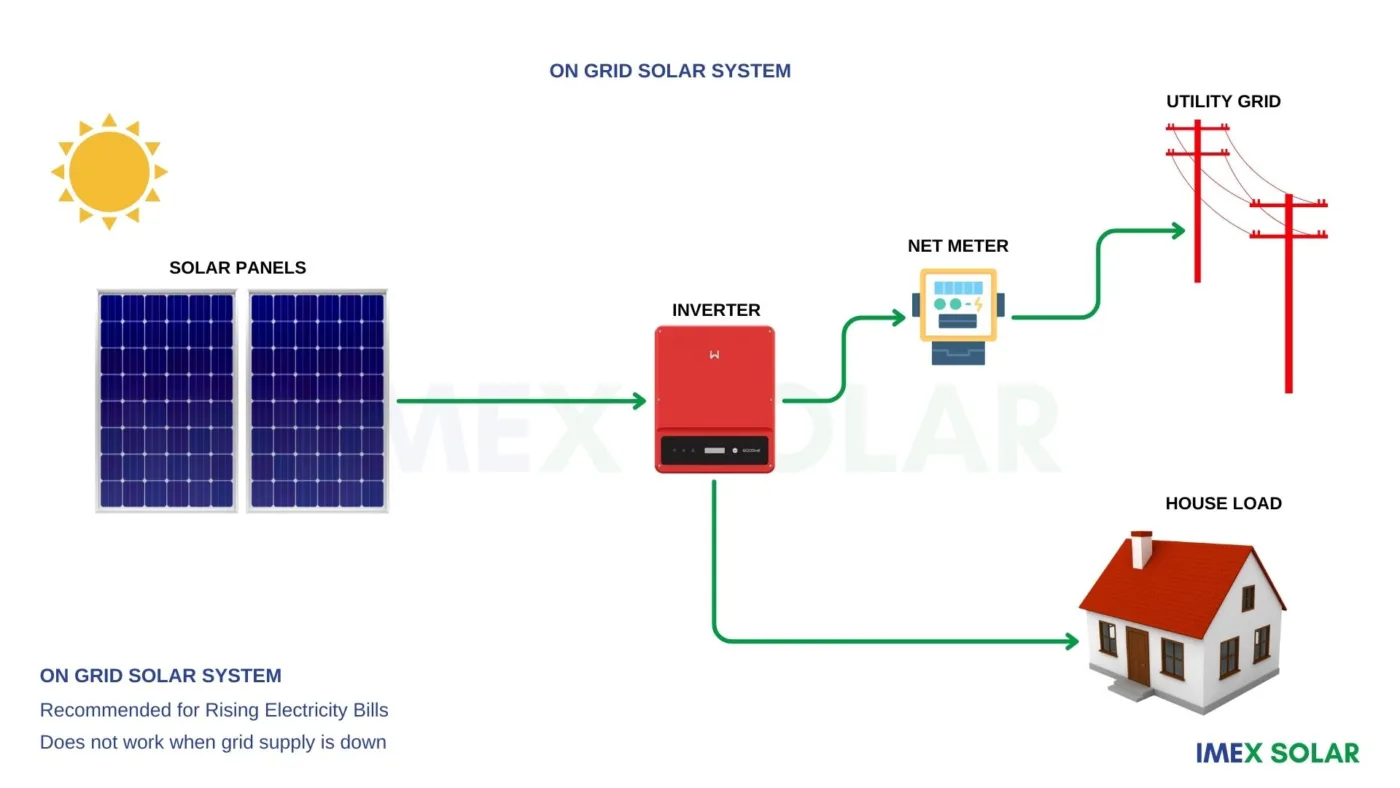
Functionality:
On-grid inverters convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity that can be used by consumer while feeding the excess power to the grid.
They can also monitor the amount of electricity generated by the solar panels and adjust the power output of the solar power system to match the energy demands of the home or business if required. In addition, on-grid inverters are designed to automatically disconnect from the grid in the event of a power outage, ensuring the safety of utility workers.
Advantages:
One of the main advantages of on-grid inverters is their ability to feed excess electricity back into the grid. This can result in significant cost savings for homeowners and businesses, as they can sign an enter into an agreement with utility company to sell excess power to the grid. There are several schemes of agreements the consumer can select: Net Metering, Net Accounting and Net Plus.
On-grid inverters are also more affordable than off-grid inverters, making them an attractive option for those who want to install solar power systems without breaking the bank.
Disadvantages:
The main disadvantage of on-grid inverters is that they cannot provide power during a blackout. If the power grid goes down, the solar power system will automatically shut down, and homeowners and businesses will be without power until the grid is restored. In addition, on-grid inverters do not have the ability to store excess energy, meaning that any excess electricity produced by the solar panels will be sent back to the grid, rather than being stored for later use.
On Grid Inverters can again be broken down into three types based on operating principle.
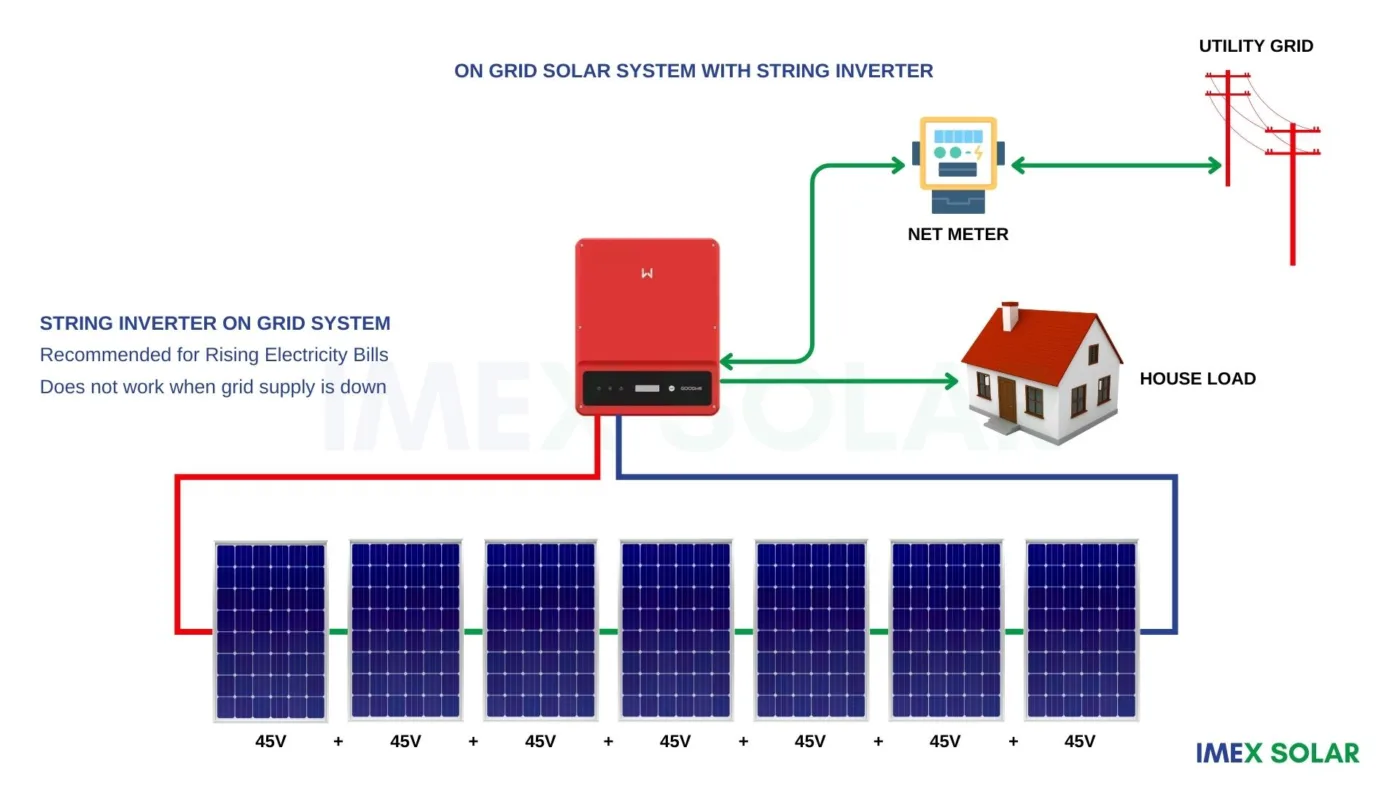
String Inverters:
String inverters are the most common type of on-grid inverter used in solar power systems. They are designed to convert the DC electricity generated by a group of solar panels, connected in series, into AC electricity that can be used by homes and businesses. String inverters are relatively affordable and easy to install, making them a popular choice for residential and commercial solar power systems.
However, one of the main disadvantages of string inverters is that they are affected by shading. If even one solar panel in a string is shaded, it can significantly reduce the output of the entire system. In addition, if a string inverter fails, it can affect the performance of the entire solar power system.
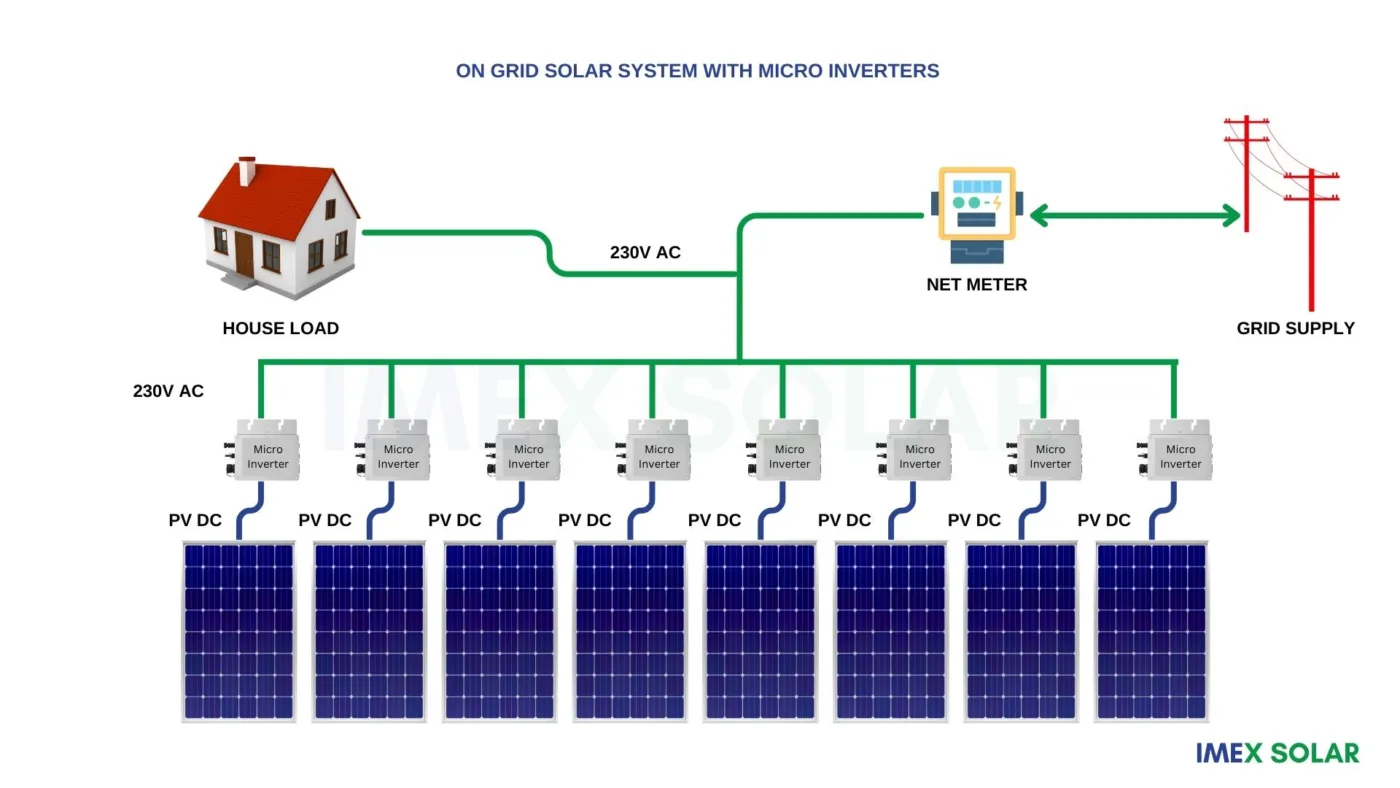
Micro inverters:
Microinverters are a newer type of on-grid inverter that are designed to convert the DC electricity generated by each individual solar panel into AC electricity. Microinverters are connected to each solar panel, and they work independently of each other. This means that even if one solar panel is shaded or not functioning properly, it will not affect the performance of the other solar panels.
Microinverters are more expensive than string inverters, but they offer several advantages. In addition to their ability to function independently, microinverters are more efficient than string inverters, as they convert DC electricity into AC electricity at the point of generation. This means that there is less energy loss during the conversion process. Microinverters are also easier to install and maintain than string inverters, as they do not require complex wiring.
Power Optimizers:
Power optimizers are a type of on-grid inverter that are similar to microinverters in that they are installed at the individual solar panel level. However, unlike microinverters, power optimizers do not convert DC electricity into AC electricity. Instead, they optimize the output of each solar panel by ensuring that the DC electricity generated is at the ideal voltage and current.
Power optimizers offer several advantages over string inverters. Like microinverters, they are not affected by shading or other issues that can affect the performance of a group of solar panels. They are also more efficient than string inverters, as they optimize the output of each solar panel. Power optimizers are also easier to install and maintain than string inverters, as they do not require complex wiring.
Off-Grid Inverters:
Off-grid inverters, also known as standalone inverters, are designed for use in solar power systems that do not require feeding power to the electricity grid. Off-grid inverters are typically used in locations where it is not feasible to connect to the grid, such as cabins, boats, and RVs or in areas the grid supply is highly unstable.
Functionality:
Off-grid inverters convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels into usable AC electricity that can be used to power homes and businesses. They also have the ability to store excess energy in batteries, which can be used during times when the sun is not shining. Off-grid inverters typically have a built-in charger that can recharge batteries from a generator or another power source when necessary.
Advantages:
The main advantage of off-grid inverters is their ability to provide power even in remote locations that are not connected to the electricity grid. They are also ideal for use in emergencies, as they can provide power during blackouts and other power outages. In addition, off-grid inverters can store excess energy in batteries, which can be used during times when the sun is not shining, making them a reliable option for those who want to reduce their reliance on traditional energy sources.
Disadvantages:
One of the main disadvantages of off-grid inverters is their cost. Off-grid inverters are typically more expensive than on-grid inverters, as they require additional components such as batteries and a generator. In addition, off-grid inverters require regular maintenance to ensure that they are functioning properly, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
On-Grid Hybrid Inverters:
On-grid hybrid inverters, also known as grid-tied with battery backup inverters, are a combination of on-grid and off-grid inverters. On-grid hybrid inverters are designed to provide the benefits of both on-grid and off-grid inverters, including the ability to feed excess electricity back into the grid and store excess energy in batteries.
Functionality:
On-grid hybrid inverters are designed to work with solar power systems that are connected to the electricity grid but also have battery backup. They are capable of converting the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity that can be used by homes and businesses. On-grid hybrid inverters can also store excess energy in batteries, which can be used during blackouts or times when the sun is not shining.
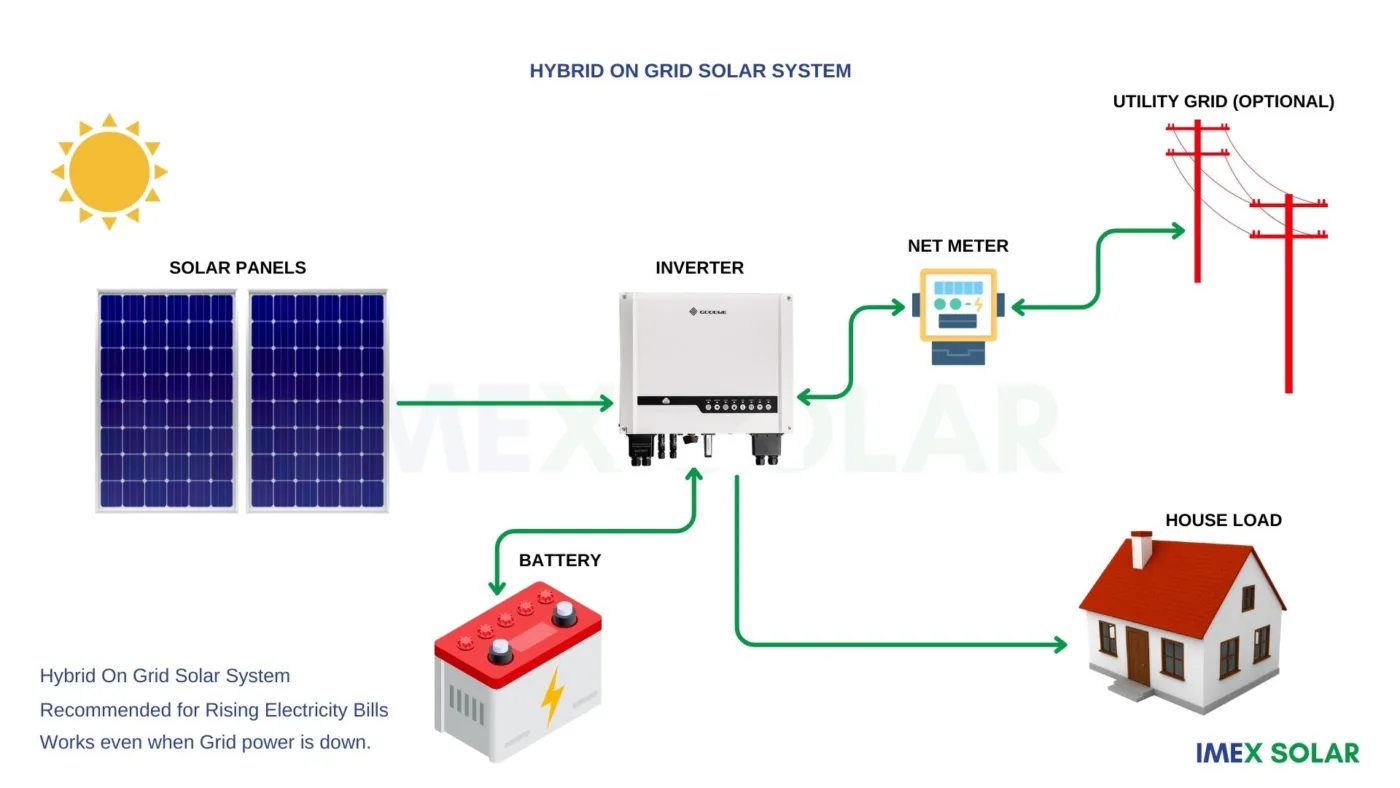
Advantages:
The main advantage of on-grid hybrid inverters is their ability to provide power during blackouts or other power outages. In addition, they offer the cost savings associated with on-grid inverters, as homeowners and businesses can earn credits for excess electricity produced by their solar power systems. On-grid hybrid inverters also provide the peace of mind of having a backup power source in case of emergencies.
Disadvantages:
On-grid hybrid inverters are typically more expensive than on-grid inverters and off-grid inverters, as they combine both on grid and off grid inverter functions in single unit. In addition, they require regular maintenance to ensure that they are functioning properly.
Solar inverters are a crucial component of solar power systems, converting the DC electricity generated by solar panels into usable AC electricity. The three main types of solar inverters are on-grid, off-grid, and on-grid hybrid inverters, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. On-grid inverters are ideal for those who want to reduce their electricity bills and earn credits for excess electricity produced by their solar power systems. Off-grid inverters are ideal for those who live in remote locations where it is not feasible to connect to the electricity grid. On-grid hybrid inverters offer the benefits of both on-grid and off-grid inverters, including the ability to feed excess electricity back into the grid and store excess energy in batteries.
When choosing a solar inverter, it is essential to consider factors such as the size of the solar power system, the energy demands of the home or business, and the cost of the inverter and associated components. It is also important to choose a reputable manufacturer and ensure that the inverter is compatible with the solar panels and other components of the solar power system.
