No products in the cart.
Resources
SOLAR CHARGE CONTROLLERS? MPPT VS PWM
“Investing in a quality solar charge controller is a wise decision that can save you money in the long run by extending the life of your battery and improving the performance of your solar energy system.”
In recent years, solar power has emerged as a widely popular and efficient alternative energy source. The solar charge controller is one of the most important components of a solar energy system. The solar charge controller regulates the flow of energy from the solar panel to the battery. In this article, we explore the significance of solar charge controllers, their various types, their operating principles, and the factors to consider when selecting one.
A solar charge controller is a critical element of a solar energy system because it prevents the battery from being overcharged and over discharged. Overcharging can harm the battery and shorten its lifecycle, while over discharging can harm the battery and reduce its capacity. A solar charge controller ensures that the battery is charged at the optimal voltage and current levels, thereby extending its lifespan and ensuring its best performance.
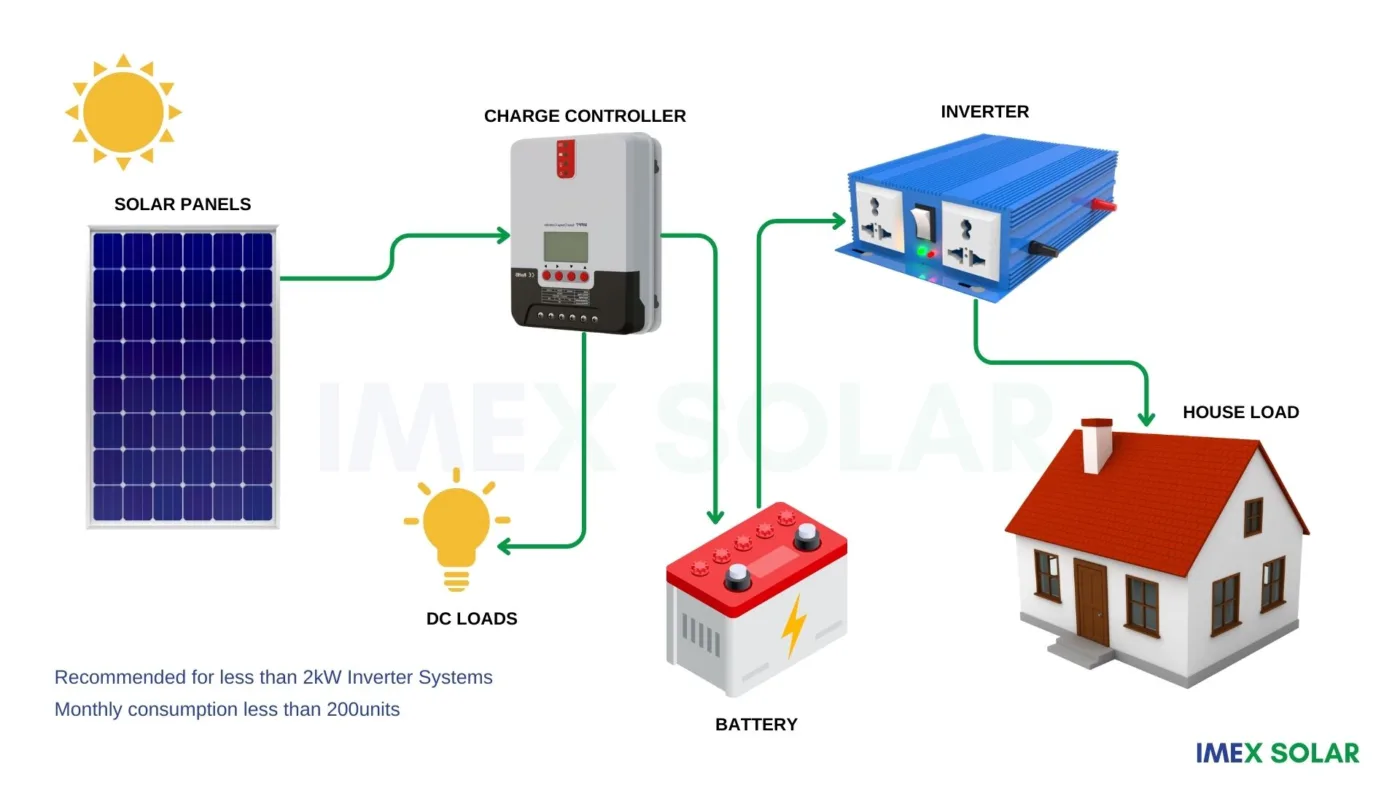
TYPES OF SOLAR CHARGE CONTROLLERS?
There are two main types of solar charge controllers available in the market, namely,
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
- MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking)
PWM controllers are simple and inexpensive, but less efficient than MPPT controllers. MPPT controllers are more efficient, feature rich but more expensive than PWM controllers.
PWM Solar Charge Controllers:
PWM solar charge controllers are the most common and simplest form of solar charge controllers. They function by modulating the solar panel voltage to match the battery voltage. PWM controllers are cheaper than MPPT controllers, but they are also less efficient. Small solar systems with low power requirements are a perfect fit for PWM controllers.
PWM controller functions by regulating the voltage of the solar panel to match the voltage of the battery. When the battery is fully charged, the PWM controller reduces the voltage to prevent overcharging. When the battery is discharged, the PWM controller increases the voltage to make sure the battery is fully charged.
MPPT Solar Charge Controllers:
MPPT solar charge controllers are more complex and more efficient than PWM controllers. They work by tracking the maximum power point of the solar panel and adjusting the voltage and current to match the battery’s requirements. MPPT controllers are more expensive than PWM controllers, but they are also more efficient, which means that they can generate more energy from the same solar panel. MPPT controllers are best suited for larger solar systems that have high power requirements.
MPPT controllers track the solar panel’s maximum power point in order to function. Maximum power point is the point in which the solar panel generates the most power. MPPT controllers changes the voltage and current according to the requirements of the battery, ensuring that the battery is charged with maximum efficiency.
How to Choose the Correct Solar Charge Controller
When choosing a solar charge controller, there are several factors to consider.
These include:
- Battery Voltage: The solar charge controller should be compatible with the battery voltage of the solar system. The most common battery voltages for solar systems are 12V, 24V, and 48V.
- Battery Type: Not all solar charge controls support all types of batteries, Li Ion, solar tubular, gel, lead acid etc. It is important that your charge controller is compatible with the battery type or it could seriously damage the batteries or cause fire hazards.
- Solar Panel Wattage: The solar charge controller should be able to handle the wattage of the solar panel. The controller should be rated for the same or higher wattage than the solar panel.
- Protection Features: The solar charge controller should have protection features to protect the battery from overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits. Some controllers also have protection against reverse polarity and lightning.
- Type of Solar Charge Controller: The type of solar charge controller depends on the size and power requirements of the solar system. PWM controllers are best suited for small solar systems, while MPPT controllers are best suited for larger solar systems.
- Efficiency: The efficiency of the solar charge controller is an important factor to consider. MPPT controllers are more efficient than PWM controllers, which means that they can generate more energy from the same solar panel.
- Features: Another factor to consider is the display and monitoring features of the solar charge controller. Some controllers have a display that shows the battery voltage, charging current, and other important information. This can be useful for monitoring the performance of the solar energy system. Some controllers also have monitoring features that allow you to monitor the performance of the system remotely.
- Wiring: It is also important to consider the installation and wiring requirements of the solar charge controller. Some controllers are easy to install and require minimal wiring, while others require more complex installation and wiring. It is important to choose a controller that is easy to install and meets the wiring requirements of the solar energy system.
- Price: The price of the solar charge controller is an important factor to consider. PWM controllers are less expensive than MPPT controllers, but MPPT controllers are more efficient and can generate more energy from the same solar panel. It is important to balance the efficiency and cost when choosing a solar charge controller.
- Brand and Warranty: It is important to choose a reputable brand that offers a warranty for their products. A warranty provides peace of mind and ensures that the product is of good quality.
- The temperature: Range in which the solar charge controller will operate. Some controllers are designed to operate in a wide temperature range, while others are only suitable for a narrow temperature range. It is important to choose a controller that is suitable for the temperature range of the location where the solar energy system will be installed.
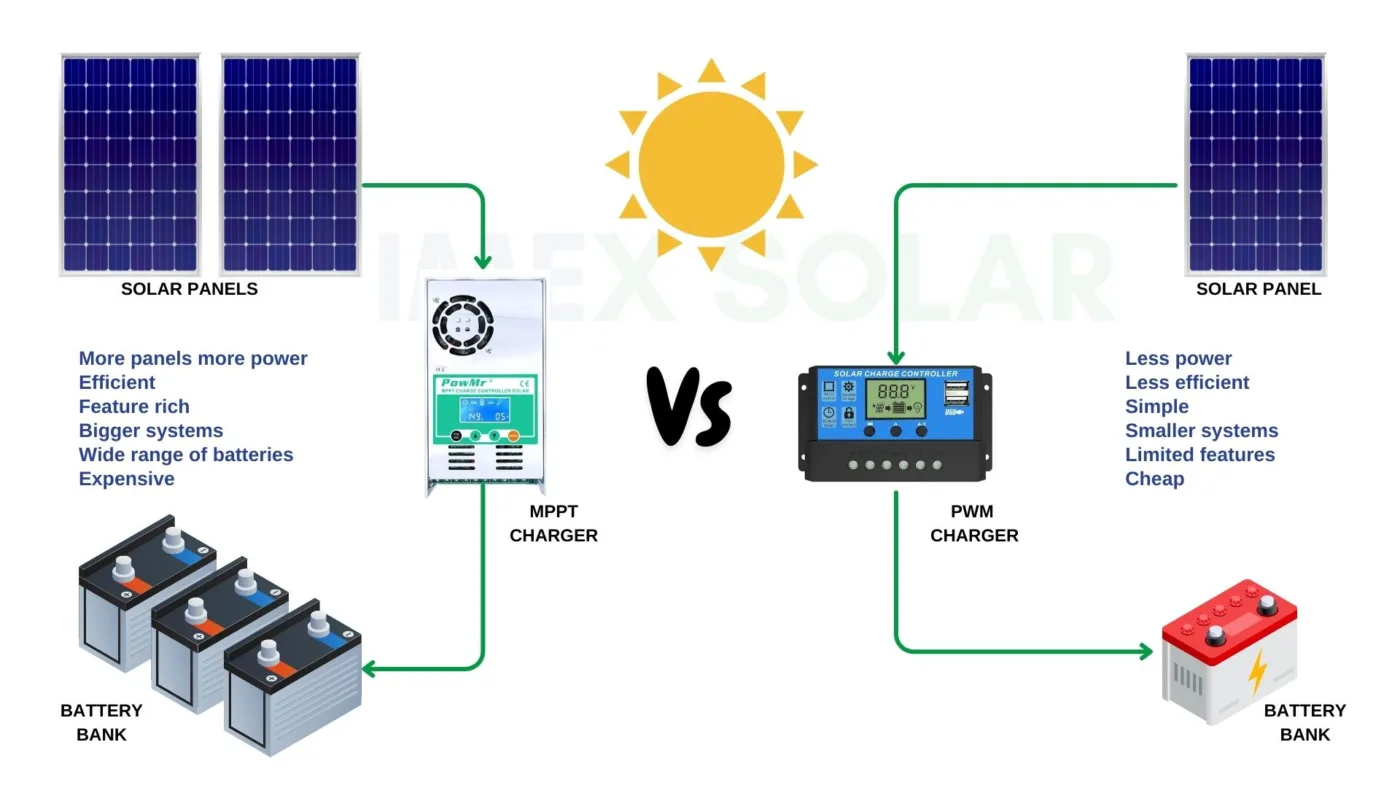
MPPT VS PWM SOLAR CHARGE Controllers, COMPARISON
- Efficiency: MPPT controllers are more efficient than PWM controllers as they can extract maximum power from the solar panel.
- Solar Panel Compatibility: MPPT controllers are compatible with a wide range of solar panels, while PWM controllers are limited to a specific range of solar panels.
- Voltage: MPPT controllers can handle higher voltage solar panels and batteries, while PWM controllers are designed for lower voltage solar panels and batteries.
- Cost: MPPT controllers are more expensive than PWM controllers due to their advanced technology and higher efficiency.
- Temperature Range: MPPT controllers can operate in a wider temperature range than PWM controllers.
- Charging Modes: MPPT controllers have multiple charging modes, while PWM controllers only have one charging mode.
- Flexibility: MPPT controllers can be used in a variety of solar energy systems, while PWM controllers are limited to smaller solar energy systems.
- Power Output: MPPT controllers can produce more power output than PWM controllers, which is useful in larger solar energy systems.
- Battery Life: MPPT controllers can extend the life of the battery by preventing overcharging and over-discharging, while PWM controllers do not have this feature.
- Monitoring: MPPT controllers have more monitoring features than PWM controllers, allowing for better performance tracking and optimization.
- Noise: PWM controllers produce more noise than MPPT controllers due to the use of a switch-mode circuit.
- Light Sensitivity: MPPT controllers are less sensitive to changes in light than PWM controllers, which can lead to better performance in changing weather conditions.
- Wiring: MPPT controllers require thicker wiring than PWM controllers due to the higher voltage and power output.
- Complexity: MPPT controllers are more complex than PWM controllers, which can make installation and maintenance more challenging.
- Compatibility with Inverters: MPPT controllers are more compatible with inverters than PWM controllers, which can be important in larger solar energy systems.
In conclusion, solar charge controllers are an essential component of a solar energy system. They protect the battery from overcharging and over-discharging, ensuring that the battery lasts longer and operates more efficiently. When choosing a solar charge controller, it is important to consider factors such as battery voltage, solar panel wattage, type of controller, efficiency, price, protection features, brand, warranty, temperature range, display and monitoring features, and installation and wiring requirements.
By choosing the right solar charge controller, you can ensure that your solar energy system operates at maximum efficiency and provides reliable power for years to come.
